New Article
Narration: Definition, Types and Examples
- March 16, 2023
- Posted by: Admin
- Category: English Grammar BPSC MP Patwari Exam MP Patwari Exam Analysis MPPSC State PSC Exams UPPSC UPSC

Narration: Definition, Types and Examples
Definition:
Narration: Reporting the words of a speaker to another is called Narration.
किसी की कही गई बात को दुसरें को बताना ही Narration कहलाता है.
दुसरे शब्दों में,
Narration शब्द का शाब्दिक अर्थ “कथन” होता है. इस शब्द का निर्माण Narrate शब्द से हुआ है. Narrate शब्द का शाब्दिक अर्थ to say / to state अर्थात कहना होता है. Narration का समानार्थक शब्द Assertion / Statement / Declaration इत्यादि होता है.
किसी के द्वारा कही बातों को व्यक्त करने के लिए इस (“….”) Punctuation marks का प्रयोग किया जाता है.
Types of Narration
ग्रामर में Narration के दो प्रकार होता है, जिसके अंतर्गत सभी रूल्स, स्पेशल नियम, change of tense रूल्स आदि का अध्ययन किया जाता है. इसे सामान्यतः Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi से संबोधित किया जाता है.
- Direct Speech /Direct Narration (प्रत्यक्ष कथन)
- Indirect Speech / Indirect Narration (अप्रत्यक्ष कथन)
1. Direct Speech किसे कहते है
प्रत्यक्ष कथन यानि Direct Speech: जब कोई श्रोता/व्यक्ति किसी वक्ता (Speaker) के कथन (Statement) को वक्ता के शब्दों में या भाषा में अभिव्यक्त करता है, उसे Direct Speech कहते है.
दुसरें शब्दों में,
जब कोई व्यक्ति वक्ता द्वारा कही गयी बातों को ज्यों का त्यों यानि हू -ब-हू किसी किसी व्यक्ति को व्यक्त करता हैं, तो उसे Direct Narration/ Speech कहा जाता है.
Note: Direct Speech के शब्दों यानि Statement को Inverted Comma (“….”) के बिच रखा जाता है.
Types of Direct Speech:
Narration में डायरेक्ट स्पीच के दो भाग होते है जिसके अनुसार कथन को हु-ब-हु या बदलकर व्यक्त किया जाता है.
- Reporting Speech
- Reported Speech
इन दो भागो का अध्ययन यहाँ विस्तार से करेंगे ताकि narration को सरलता से समझ सके.
Reporting Speech क्या है?
Direct Speech का वह भाग जो Inverted Comma (“….”) के बहार रहता है, Reporting Speech कहलाता है. जैसे;
- The teacher says, “The girl was lazy.”
- Ram said, “Sita has done her work.”
- Mohan said, ” I am busy.”
- She said, “he loves me a lot.”
दिए गए नरेशन यानि Narration उदाहरण में The teacher says, Ram said, Mohan said, or She said Reporting Speech है.
Reporting Speech के प्रकार
Narration को समझने के लिए Reporting Speech मुख्यतः तीन भागो में विभाजित किया गया है. जो इस प्रकार है:
Reporter: वक्ता अर्थात कथन या कोई बात कहने वाले को Reporter कहा जाता है. जैसे;
- She said to me, ” I had no time for you.”
- They said to us, ” We are giving a nice present.”
इस उदाहरण में she और they Reporter है.
Note: Reporter को दुसरें शब्दों में The subject of Reporting Verb भी कहा जाता है.
Reporting Verb: किसी वक्ता द्वारा जिस Verb का प्रयोग किसी कथन को करने के लिए किया जाता है, उसे Reporting Verb कहते हैं. जैसे;
- Meera said to Munni, ” you are a good girl.”
- I said to her, ” I love you so much.”
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में said Reporting Verb है.
Reporting Object:- वक्ता किसी कथन को जिससे कहता है , उस object को Reporting Object कहते हैं. जैसे;
- They said to the boys, ” you sang well.”
- He said to me, ” I can defeat you.”
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में the boys और me Reporting Object है.
Reported Speech क्या होता है?
Direct Speech का वह भाग जो Inverted Comma (“….”) के भीतर रहता है, उसे Reported Speech करते है. जैसे;
- She says to them, ” This is mine and that is yours.”
- The girl said to her mother, ” I shall obey you.”
- They said, ” We can not escape death.”
- My father said, ” Labour never goes in vain
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में Inverted Comma के अन्दर वाले वाक्य जैसे This is mine and that is yours आदि Reported Speech है.
Verb of Reported Speech: Reported Speech के verb को Verb of Reported Speech कहा जाता है. जैसे;
- She said, ” I have seen this boy before.”
- He said, ” I shall do my best.”
उपरोक्त वाक्यों में Have और Shall Verb of Reported Speech है.
Note: Direct Speech के सभी भागों को एक उदाहरण के अनुसार निम्न प्रकार समझे:
उदाहरण: The teacher said to me, ” you have done well in the examination.”
| Reporting Speech | The teacher said to me |
| Reported Speech | you have done well in the examination |
| Reporter | the teacher |
| Reporting verb | said |
| Reporting Object | me |
| Verb of the Reported Speech | have |
2. Indirect Speech किसे कहते है?
जब कोई ऑडियंस यानि वक्ता किसी Speaker के कथन को अपने शब्दों या भाषा में व्यक्त या अभिव्यक्त करता है, तो उसे Indirect Speech कहते है.
दुसरें शब्दों में,
जब किसी वक्ता के मूल कथन में हम कुछ हेर-फेर कर उसके आशय या सारांश को अपने शब्दों में व्यक्त करते है, तो उस कथन को Indirect Speech कहते है.
Note: Indirect Speech को Inverted Comma के अंदर नही रखा जाता है. जैसे;
- You said that she had written a letter.
- They said that we are social animals.
- Mukesh told her that he had been teaching her lover for years.
- He said that I had been absent in the class.
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में sentences को inverted comma से बहार रखा गया है. इसलिए, ये सभी Indirect Speech है.
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
इंग्लिश ग्रामर में Narration के वाक्यों को Direct Speech से Indirect में बदलने के लिए विभिन्न प्रकार के नियम को फॉलो करना पड़ता है. Narration के सभी रूल्स वाक्य के बनावट, Tense और Person के अनुसार अलग-अलग होते है. Narration के वाक्यों को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के दो नियम होते है:
- General Rules (सामान्य नियम )
- Special Rules (विशेष नियम )
Direct Speech को Indirect Speech में change करने के लिए कुछ General Rules और कुछ Special Rules को फॉलो किया जाता है.
General Rules वैसे Rules को कहते है, जो हर प्रकार के Sentences के साथ लागु किए जाते है, जबकि Special Rules विभिन्न प्रकार के वाक्यों के लिए अलग-अलग होता है. यहाँ General और Special Rules का अध्ययन भिन्न-भिन्न रूप में करेंगे.
1. Narration Rules
ऐसा नियम जो सभी तरह के वाक्यों में लागू होता है उसे General Rules कहते है.
जनरल रूल्स के अंतर्गत Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के निम्न नियम होते है:
1. Change of Persons
2. Change of Tenses
3. Change of Other Parts of Speech
Narration Rules in Hindi के माध्यम से Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के सभी नियम का अध्ययन निचे विस्तार से करेंगे.
Important Note:
- यदि Reporting Verb के बाद कोई Object न हो, तो Reporting Verb को नही बदला जाता है.
- लेकिन यदि Reporting Verb के बाद कोई Object हो, तो say to को tell में, says to को tells में, और said to को told में बदल दिया जाता है.
- Indirect Speech में Assertive Sentence / Affirmative Sentece को “That” से जोड़ा जाता है.
याद रखे:
| Say to | Tell |
| Says to | Tells |
| Said to | Told |
1. Change of Persons ( सर्वनाम का परिवर्तन )
Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलते समय Inverted Commas (“….”) के अंतर जितने भी Persons जैसे First, Second और Third Person रहते है, वे सभी SON फार्मूला के क्रमानुसार बदल जाते है.
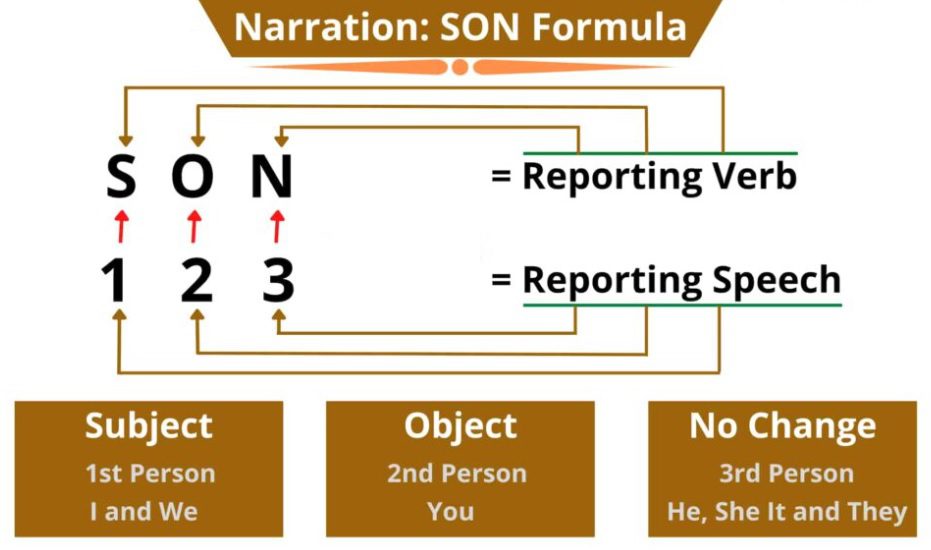
Note: SON Formula का अर्थ
| SON | Persons |
| S = Reporting Verb का Subject | 1 = First Person |
| O = Reporting Verb का Object | 2 = Second Person |
| N = No Change | 3 = Third Person |
Change of Persons के मुख्य नियम:
Rule: 1. यदि Reported Speech का Subject First Person ( I, We) का हो, तो वह Reporting Verb के Subject के Number, Person तथा Case के मुताबिक बदल जाता है. जैसे;
- Direct: he said to me, ” I am ready.”
- Indirect: He told me that he was ready.
Rule: 2. यदि Reported Speech का Subject Second Person (You) का हो, तो वह Reporting Verb के Object के Number Person तथा Case के मुताबिक change होगा. जैसे;
- Direct: he said to me, “you are late.”
- Indirect: he told me that I was late.
Rule: 3. यदि Reported Speech का Subject Third Person का हो, तो Indirect Speech में इनमे कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है. जैसे;
- Direct: You said, “She wrote a letter.”
- Indirect: You said that she had written a letter.
Rule: 4. Persons में परिवर्तन करते समय Number तथा Case में परिवर्तन नही होता है.
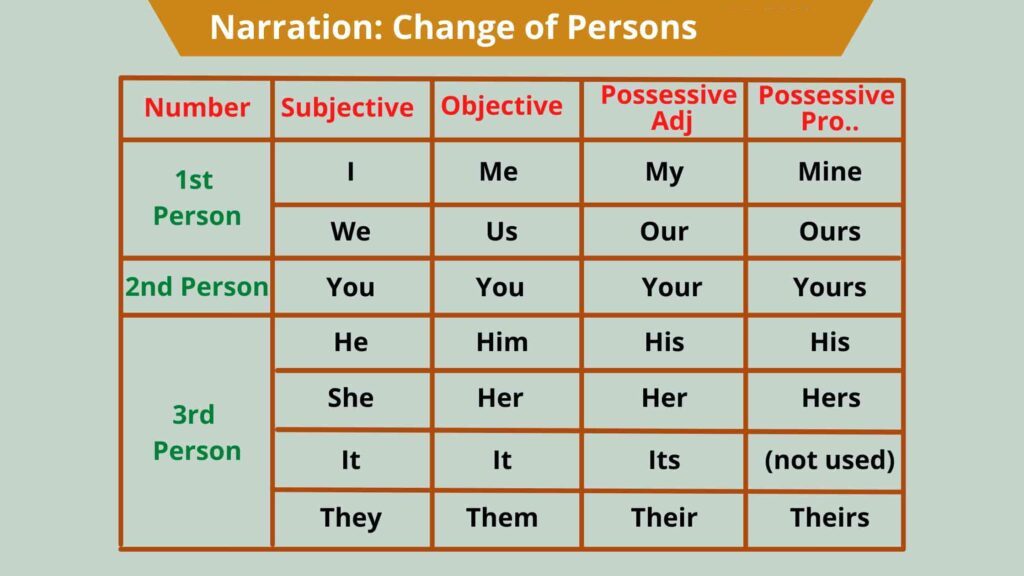
Note: ऊपर दिए गए टेबल के अनुसार ही Persons में बदलाव करे: जैसे;
- Direct: Binay says to me, “I am your friend.”
- Indirect: Binay tells me that he is my friend.
- He said to me, “I help you.” Direct
- Indirect: He told me that he helped me.
2. Narration: Change of Tenses (टेंस का परिवर्तन)
Rule: 1. यदि Reporting Verb Present या Future Tense में हो, तो Indirect Speech में Reported Speech के Tense में कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है. अर्थान, जिस Tense में Reported Speech रहता है, उसी Tense का प्रयोग ज्यों का त्यों Indirect Speech में होता है. जैसे;
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| Mohan says, “I shall go there.” | Mohan says that he will go there. |
| Vipasha says, “I went.” | Vipasha says that she went. |
| He will say tome, “I am your neighbour.” | He will say to me that he is my neighbour. |
| She will say to me, “I am ready to help you.” | She will say to me that she is ready to help me. |
| Mukesh says to Binay, “I shall help you if you help me.” | Mukesh says to Binay that he will help him if he helps him. |
Rule: 2. यदि Reporting Verb Past Tense में तथा Reported Speech Present और Past Tense में हो, तो Indirect Speech में Reported Speech का Tense निम्न प्रकार बदला जाता है.
Note: Tense में परिवर्तन का ट्रिक: “Present का जिसमे, Past का उसमे”
| Direct Narration | Indirect Narration |
|---|---|
| Present Indefinite Tense | Past Indefinite Tense |
| Present Continuous Tense | Past Continuous Tense |
| Present Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Tense |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Past Indefinite Tense | Past Perfect Tense |
| Past Continuous Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Past Perfect Tense | No Change |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | No Change |
| Future Tenses | No Change |
लेकिन यदि Reporting Verb Past Tense में हो तथा Reported Speech Future में हो, तो Indirect Speech में वाक्य इस प्रकार बदलता है:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| Shall | Should |
| Will | Would |
| Shall be | Should be |
| Will be | Would be |
| Shall have | Should have |
| Will have | Would have |
| Shall have been | Should have been |
| Will have been | Would have been |
For Examples:
- Direct: He said to me, “I shall write a letter.”
- Indirect: He told me that he should write a letter.
- He said to me, “I shall be writing a letter.”
- Indirect: He told me that he should be writing a letter.
Narration: Verb में Changes
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| Shall | Should |
| Will | Would |
| Can | Could |
| Am / Is / Are | Was / Were |
| Have / Has | Had |
| Was / Were | Had been |
| Had to + Verb 1st Form | Had had to + Verb 1st Form |
| Could | No Change |
| Should | No Change |
| Would | No Change |
| Might | No Change |
Examples:
| Direct Narration | Indirect Narration |
| Ramesh said to Shila, “You can speak English.” | Ramesh told Shila that he could speak English. |
| He said to you, “You may go out. | He told you that you might go out. |
| Sweta said to Vipasha, ” I am a good girl.” | Sweta told Vipasha that she was a good girl. |
| She said to me, “I have no time for you.” | She told me that she had no time for me. |
| She said to me, ” You have to do this word.” | She told me that I had to do that work |
3. Change of Other Parts of Speech
यदि Reported Verb Past Tense में हो, तो Reported Speech में प्रयुक्त निकटता के अर्थ सूचक शब्दों को दुरी के अर्थ सूचक शब्दों में Indirect Speech में बदल दिया जाता है. जैसे;
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Hence | Thence |
| Now | Then |
| Thus | So |
| Today | That day |
| Yesterday | The previous day The day before |
| The day before yesterday | Two days before |
| Tomorrow | The next day The following day On the morrow |
| To night | That night |
| This day | That day |
| The day after tomorrow | In two days, Time |
| Last week | The previous week The week before |
| Last month | The previous month The month before |
| Last night | The previous night The night before |
| Last year | The previous year The year before |
| Last day | The previous day The day before |
| Next week | The following week |
| Next month | The following month |
| Next year | The following yaer |
| Next night | The following night |
| Next day | The following day |
| Come | Go |
| A year ago | A year before |
Note: Reported Speech में प्रयुक्त निकटता सूचक शब्दों से यह ज्ञात हो कि प्रयुक्त वस्तु/जगह/समय/परिस्थिति/वक्ता के साथ Present Tense में मौजूद है. ऐसी स्थिति में निकटता सूचक शब्दों को दुरी सूचक शब्दों में नही बदलता जाता है. जैसे;
1. Mohan said, “This is my book.”
Moahn said that this was his book.
2. This morning she said, “I will go out today.”
This morning she said that she would go out today.
उदाहरण में निकटम सूचक शब्द है, लेकिन वाक्य Present Tense में है. इसलिए, This और Today को दुरी सूचक शब्दों में नही बदला गया है.
Tense Narration Rules
Rule: यदि Reporting Speech, Past Tense में हो और Reported Speech सार्वभौमिक तथ्य (Universal Truth), आदतन सत्य (Habitual Facts), ऐतिहासिक सत्य (Historical Facts), या कहावत से सम्बंधित हो, तो Indirect Speech में उनके Tense या Verb Form को नही बदला जाता है. जैसे;
Universal Truth:
- The teacher said, “The sun rises in the East.”
- The teacher said that the sun rises in the East.
Habitual Facts:
- He said, ” I walk in the morning.”
- He said that he walks in the morning.
Historical Facts:
- The Prime Minister said, ” Indian got freedom in 1947.”
- The Prime Minister said that India got freedom in 1947.
Proverb:
- Mukesh said to me, ” Honesty is the best policy.”
- Mukesh told me that honesty is the best policy.
2. Special Rules in Narration
वे रूल्स जो भिन्न-भिन्न प्रकार के Sentences यानि वाक्यों के लिए भिन्न-भिन्न होते है. उसे Narration में Special Rules कहते है.
Reported Speech में अर्थात Inverted Commas के भीतर Assertive Sentence, Imperative Sentence, Interrogative Sentence, Optative Sentence, Exclamatory Sentence का प्रयोग होने पर Special Rules को फॉलो किया जता है.
ऐसे वाक्यों में एक ही प्रकार के नियमों का पालन करने से Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने पर गलती होने की संभावना अधिक होती है. इसलिए, ऐसे वाक्यों का Narration, स्पेशल रूल्स से किया जाता है.
Special Rules के प्रकार:
Narration में Special Rules का प्रयोग 5 प्रकार के वाक्यों को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए किया जाता है.
- Assertive Sentence
- Imperative Sentence
- Interrogative Sentence
- Optative Sentence
- Exclamatory Sentence
1. Assertive Sentence: Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में अर्थात, Inverted Commas के अन्दर Assertive Sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में निचे दिए गए नियम के अनुसार बदला जाएगा.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verbs – say to, says to, said to को क्रमशः tell, tells, told में बदल दिया जाता है. लेकिन say , says, said यानि बिना “to” वाले वर्ब को tell, tells, told में नही बदला जाता है.
Note: tell, tells, told, Transitive Verbs है, इसलिए, इनके बाद Object का प्रयोग आवश्यक किया जता है. To का प्रयोग tell, tells, told के बाद नही होता है. जैसे;
- Direct: She says to her husband, “You must come come back home in time.”
- Indirect: She tells her husband that he has to come back home in time.
Rule: 2. Inverted Commas को हटाकर, इसके बदले That का प्रयोग किया जाता है.
Rule: 3. Assertive Sentence में General Rules को फॉलो किया जाता है. जैसे;
| Direct Narration | Indirect Narration |
| My friend says to him, “You are not a wise man.” | My friend tells him that he is not a wise man. |
| She says, “I shall write a letter.” | She says that she should write a letter. |
| They say, “We are reading novels.” | They say that they are reading novels. |
| Vipasha will say to me, “I want to buy an item of gold.” | Vipasha will tell me that she wants to buy an itme of gold. |
| Mohan said, “I can buy a car.” | Mohan said that he could buy a car. |
Rule: 4. यदि Reported Speech में must का प्रयोग हो तथा must से नैतिक कर्तव्य/जिम्मदारी/नियम/सिद्धांत आदि का बोध हो, तो Indirect Speech में must का प्रयोग ज्यों का त्यों होता है. अर्थात, ऐसे वाक्यों में कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है. जैसे;
- Direct: He said, “One must do one’s duty.”
- Indirect: He said that one must do one’s duty.
Rule: 5. यदि Reported speech में स्वागत या विदाई सूचक शब्दों जैसे Good Morning, Good Evening, Good night आदि का प्रयोग हो, तो इसे Indirect में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
| Step: 1. | Subject of Reporting Verb के बाद अर्थ के मुताबिक bid/bids/bade, wish/wishes/wished का प्रयोग करे. |
| Step: 2. | इसके बाद Object of Reporting Verb का प्रयोग करे. |
| Step: 3. | Object of Reporting Verb के बाद Good morning आदि जैसे शब्दों का प्रयोग करे. |
| Step: 4. | इसके बाद and said that का प्रयोग करे. |
| Step: 5. | Persons को change करने के लिए General Rules को फॉलो करे. |
Examples:
- Direct: My classmate said to me, “Good morning, You have finished your home work.
- Indirect: My classmate wished me good morning and said that I had finished my home work.
2. Interrogative Sentence: Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में अर्थात, Inverted Commas के अन्दर Yes-No Questions या WH-Questions का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस नियम के अनुसार बदला जाता है.
दरअसल, Interrogative Sentences दो प्रकार से बनाया जाता है. जैसे ऊपर दर्शाया गया है. ऐसे वाक्यों का अनुवाद Indirect Speech में करने के लिए अलग-अलग नियम को फॉलो किया जाता है.
Yes-No Questions: Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में वाक्य Helping Verb or Auxiliary Verb से शुरू हो, तो उसे Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए निम्न नियम को फॉलो किया जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verb – say/says to, says / says to, said / said to, को Sentence के अर्थ के अनुसार ask / demand / enqure / want to know, asks / demands / enquires / wants to know, asked / demanded / enquired / wanted to know में बदल दें.
- Inverted Commas के बदले if या Whether का प्रयोग करे
- Interrogative Sentence को Assertive Sentence में change करे.
- Persons को change करने के लिए General Rules को फॉलो करे.
Interrogative to Assertive Rules:
| Interrogative Sentences | Assertive Sentences |
| Do you go? | You go. |
| Did she go? | She went. |
| Can he not speak? | He can not speak. |
| Where do you live? | Where you love. |
| Who wrote the Ramayana? | Who the Ramayana rote. |
Note:
- demand / want to know के बाद Object के पहले of preposition का प्रयोग होता है.
- Whether का प्रयोग एग्जाम में ज्यादातर होता है. इसलिए, If के बदले Whether का प्रयोग करे.
- Question marks के बदले Full Stop का प्रयोग करे.
Examples:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| He said to me, “Are you a student?” | He asked me if/whether I was a student. |
| She said to Raman, “Have you a mobile set?” | She enquired of Raman if/where he had a mobile set. |
| Mukesh said to me, “Did you teach my sister?” | Mukesh asked me if/where I had taught her sister. |
| Sneha said to me, “Do you play cricket?” | Sneha asked me if/whether I played cricket. |
| Ajit said to Vipasha, “Do you know the way?” | Ajit asked Vipasha if/whether she knew the way. |
| Ranjani said to me, “Can you meet me tomorrow at Patna Junction?” | Ranjani asked me if/whether I could meet her the next day at Patna Junction |
| He said to us, “Are you going away today?” | He asked us if/whether we were going away that day. |
WH-Questions: Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reporting Speech में अर्थात Inverted Commas (“….”) के भीतर Wh-Questions का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verbs को sentence के अर्थ तथा Tenses के मुताबिक ask / asks / asked, enquire / enquires / enquired, demand / demands / demanded, want to know आदि में बदले.
- Inverted Commas को हटा कर if / whether आदि का प्रयोग न करे. जिस Interrogative Words / Interrogative Pronouns का प्रयोग हो, उसे ज्यों का त्यों प्रयोग करे.
- Interrogative Sentence को Assertive Sentence में change करे.
- Persons को change करने के लिए General Rules को फॉलो करे.
- अंत में Full Stop का प्रयोग करे.
Note: asked के बाद प्रयुक्त Object के पहले of का प्रयोग नही होता है.
Examples:
| Direct Narration | Indirect Narration |
| I said to my wife, “What are you doing today?” | I asked my wife what she was doing that day. |
| He said to me, “When will you return?” | He asked me when I would return. |
| She said, “Who went there?” | she asked who had gone there. |
| I said to her, “What happened?” | I asked what had happened. |
| I said to her, “Which class do you read in?” | I asked her which class she read in. |
| I said to him, “Why did you insult my brother?” | I demanded of him why he had insulted my borther. |
| Anshu said to her mother, “How are you?” | Anshu asked her mother how she was. |
3. Imperative Sentences: Narration
सामान्य रूप से Imperative Sentences से order, command, request, pray, suggest आदि का बोध होता है. जैसे; Bring a glass of water. आदि.
यदि Reported Speech में Imperative sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verbs- Say, Says, Said के बदले निचे दिए गए words को अर्थ के अनुसार बदले:
| Say | Says | Said |
| Order | Orders | Ordered |
| Request | Requests | Requested |
| Ask | Asks | Asked |
| Beg | Begs | Begged |
| Tell | Tells | Tolt |
| Command | Commands | Commanded |
| Warn | Warns | Warned |
| Advise | Advises | Advised |
| Suggest | Suggests | Suggested |
| Implore | Implores | Implored |
Imperative Verb
| Verbs | Hindi Meaning |
| beg | मांगना |
| order | आज्ञा देना |
| request | प्रार्थना करना, विनती करना |
| warm | चेतावनी देना |
| implore | विनती करना |
| entreat | किसी वस्तु का मांग करना |
| urge | विनती करना |
| threaten | धमकी देना |
| command | आदेश देना |
Rules: 2.
- Inverted Commas को हटाकर “to” का प्रयोग करे.
- Inverted Commas के अन्दर संबोधन के रूप में किसी Noun का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Reporting Verb का Object बना दें.
- Reporting Verb के बाद Object का प्रयोग रहे या ना रहे Indirect Speech में Reporting Verb के बाद Object का प्रयोग अवश्य करे.
- Please, Kindly, Sir, Madam को हटा दें.
- Sir, Madam के स्थान पर Respectfully का प्रयोग करे.
- Reporting Verb के बाद object का प्रयोग हो, तो Sir, madam के स्थान पर Respectfully का प्रयोग object के बाद किया जाता है.
- persons को बदलने के लिए जरूरत के मुताबिक General Rules का प्रयोग करे.
Examples:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| He said to Pankaj, “Sit down.” | He told Pankaj to sit down. |
| The teacher said to the students, “Keep quiet.” | The teacher asked the students to keep quiet |
| The doctor said, ” Walk in the morning.” | The doctor advised me to walk in the morning. |
| The student said to the director, “Sir, please grant me leave for five days.” | The student requested the director respectfully to grant him leave for five days. |
| She said, ” Madam, I have a T.V set.” | She said respectfully that she had a T.V. set. |
Negative Imperative Sentence
सामान्तः Negative Imperative Sentence “Don’t से शुरू होता है.
Reported Speech में Negative Imperative Sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदले:
Rule: 1.
- Reporting Verb-say, says, said को अर्थ के अनुसार ask/asks/asked, tell, tells, told आदि में बदलें
- Inverted Commas को हटा कर not to का प्रयोग करे.
- जरुरत के मुताबिक General Rules का प्रयोग करे.
Examples:
1. He said to me, “Don’t open the door.”
He asked me not to open the door.
2. He said to me, “Don’t disturb me.”
He asked me not to disturb him.
Imperative Sentence Forbid का प्रयोग
Reporting Verb को Forbid/forbids/forbade में अर्थनुसार बदल कर और Inverted Commas के बदले to का प्रयोग करे. जैसे;
- Direct: The teacher said to the student, “Don’t make a noise in the class.”
- Indirect: The teacher forbade the student to make a noise in the class.
Let से शुरू होने वाले वाक्य का Indirect Speech
यदि Let से शुरू होने वाले Imperative Sentence से प्रस्ताव या सुझाव का बोध हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
| Step: 1. | Reporting Verb – say, says, said को propose/suggest में टेंस के फॉर्म के अनुसार change करे |
| Step: 2. | Inverted Commas को हटाकर that का प्रयोग करे |
| Step: 3. | let हटा दें |
| Step: 4. | Objective Case के Pronouns “us” को sentence के अर्थ / भाव के अनुसार Nominative Case के Pronouns We / They में change करे |
| Step: 5. | We / They के बाद should + v1 का प्रयोग करे. |
Note:
- Propose या suggest के बाद Object का प्रयोग करना हो, तो propose या suggest के बाद तथा object के पहले “to” preposition का प्रयोग निश्चित रूप से होता है.
- we का प्रयोग उस समय करना चाहिए जब Reported स्वयं प्रस्तावित कार्य में शामिल हो.
Examples:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| Mohan said to his friends, “Let us go the cinema.” | Mohan proposed / suggested to his friends that we/they should go to cinema. |
| I said to the villagers, “Let us help the poor.” | I proposed to the villagers that we should help the poor. |
| The children said, “Let us play together.” | The children suggested that we should play together. |
| He said, “Let us work for the Nation.” | He proposed that they should work for the Nation. |
| He said, “Let’s go for a walk.” | he suggested going for a walk. |
Let + Wish or Desire वाले वाक्यों का Indirect Speech
यदि Let से शुरू होने वाले Imperative Sentence से wish / desire का बोध हो, तो उसे Indirect speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
Rule: 1.
- Reporting Verb को wish / wishes / wished में change करे.
- Inverted Commas के बदले that का प्रयोग करे.
- Let को वाक्य से हटा दें.
- Let के बाद प्रयुक्त Objective Case के Pronouns को Nominative Case में change करे.
- Nominative Case के Pronouns – I, she, he आदि के बाद should +V1 का प्रयोग करे. जैसे
| Direct Narration | Indirect Narration |
| Mukesh said, “Let me go out.” | Mukesh wished that he should go out. |
| Veena said, “Let him be my husband.” | Veena wished that he should be her husband. |
| She said, “Let me live with him.” | She wished that she should live with him. |
| You said, “Let me do what I like.” | You wished that you should do what you like. |
| The teacher said, “Let me help the students.” | The teacher wished that he should help the students. |
4. Optative Sentence का Indirect Speech
सामान्यतः Optative sentence के वाक्यों से इच्छा, अभिशाप, आशीर्वाद आदि जैसे भावों का बोध होता है.
यदि Reported Speech में Optative sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसका Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi निम्न प्रकार बनाया जाता है.
Rule: 1.
- say, says, said को sentence के अर्थ के अनुसार wish/wished/pray/curse आदि में change करे.
- Inverted Commas के बदले that का प्रयोग करे.
- may को might में change करे.
- Exclamation mark (!) के बदले Full Stop का प्रयोग करे.
- Persons को change करने के लिए General Rules को फॉलो करे. जैसे;
Note:
यदि Optative sentence “May” से शुरू न हो, तो “may” को understood करके Indirect speech में बदलना चाहिए. अर्थात, वाक्य में might का प्रयोग करना चाहिए.
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| He said, “May Got help you!” | He prayed that God might bless me. |
| Mother said to me, “May you love long!” | Mother blessed me that I might live long. |
| They said to him, “May you get success!” | They wished me that he might get success. |
| Manisha said to me, “May you die!” | Manisha cursed me that I might die. |
| The saint said, “May God help you!” | The saint prayed that God might help me. |
| He said to me, “You be happy!” | He wished me that I might be happy. |
| They said, “Long live our democracy!” | they wished that their democracy might live long. |
| My grandfather said to me, “You live in peace!” | My grandfather wished me that I might live in peace. |
5. Exclamatory Sentence: Narration
सामान्यतः exclamatory sentence से हर्ष, घृणा, आश्चर्य, प्रसंशा, संदेह, क्रोध, तिरस्कार, पश्चाताप, आदि जैसे मानसिक भावनाओं का बोध होता है. इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में Oh !, Ah !, Alas !, Hurrah !, Bravo !, Well done!, आदि का प्रयोग भी होता है.
Note: ऐसे वाक्यों में What और How का भी प्रयोग होता है.
Exclamatory Sentence का Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए निम्न प्रक्रिया को फॉलो किया जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verb – say/says/ said को sentence के अर्थ के अनुसार exclaimed with joy / exclaimed with sorrow आदि में change करे.
Note: Exclamatory Sentence में प्रयुक्त exclamatory words:
| Exclamatory Words | English Meaning | Hindi Meaning |
| Hurrah! | Joy | हर्ष/ख़ुशी |
| Oh ! Alas ! Ah ! Oh dear ! | Sorrow | दुःख |
| Ha ! ha ! | Amusement | मनोरंजन |
| Fie ! Fie ! | Reproof | निंदा / अस्वीकृति |
| My goodness ! Good gracious ! | Surprise | आश्चर्य |
| Bother ! Bother it! | Annoyance | तंग |
| Bravo ! | Approval | स्वीकृति |
| Stuff ! bosh ! Tut ! Tut ! Tush ! | Ridicule | घृणा / उपहास |
| Hi ! Holloa ! | To call someone | किसी को बुलाना |
| Hum ! hem ! Humph ! | Doubt | संदेह |
| Oh dear ! | Sorrow | दुःख |
| Confound you ! | Anger | क्रोध |
| Ugh ! | Disgust | नफरत / घृणा |
| Good heavens ! | Horror | आतंक / भय |
| Well done ! | praise | प्रशंसा / गुणगान |
| My God ! | Surprise | आश्चर्य |
| You mischief monger ! | Contempt | तिरस्कार |
| Hello ! | Greet | स्वागत |
| Good morning ! Good night ! | bid | आमंत्रण |
| Ahorse | Exclaim | आश्चर्य |
| Help ! | Shout for help | मदद के लिए बुलाना |
- Inverted Commas को हटाकर that का प्रयोग करे
- Interjectional Words – oh, ah, alas जैसे words को हटा दें.
- Exclamation marks को हटाकर full stop का प्रयोग करे.
Note: Exclamatory Sentence को Assertive sentence में change इस प्रकार करे.
| What + Noun = What a fool ! | Adjective + Noun A big / great fool. |
| What + Adj + Noun = What a fine place ! | Very + Adj + Noun A very fine place. |
| How + Adj / Adverb = How beautiful she is ! | Very + Adj / Adverb She is very beautiful. |
Examples:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| Vipasha said, “Alas ! I am ruined.” | Vipasha exclaimed with sorrow that she was ruined. |
| Mukesh said, “What a beautiful girl she is!” | Mukesh exclaimed with joy that she was a very beautiful girl. |
| He said, “Ah ! My dog is dead.” | He exclaimed with sorrow that his dog was dead. |
| The player said, “Ah ! I have lost the game.” | The player exclaimed with sorrow that he had lost the game. |
| He said, “Nonsense !” | He exclaimed that it was nonsense. |
| He said, “What a place!” | He exclaimed with joy that it was a very fine place. |
| She said, “How happy I am !’ | She exclaimed with joy that she was very happy. |
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
| He will say to me, “I am fine.” | He will tell me that he is fine. |
| He said, “Honesty is the best policy.” | He said that honesty is the best policy. |
| Dad said to Pankaj, “I will not give you pocket money.” | Dad told Pankaj that he would not give him pocket money. |
| My friend said, “I have been to England thrice.” | My friend said that he had been to English thrice. |
| He said, “I can run faster than Ravi.” | He said that he could run faster than Ravi. |
| He said, “I should meet you in the evening.” | He said that he should meet me in the evening. |
| The teacher said to Rehman, “Stand up right now.” | The teacher ordered/instructed Rehman to stand up right then. |
| She said to her husband, “Please speak the truth.” | She requested her husband to speak the truth. |
| Boss said, “Follow me”. | Boss ordered/instructed to follow him. |
| The Principal said to us, “Don’t make a noise.” | The Principal instructed/ordered us not to make a noise. |
| My uncle said, “Well done! You have done a good job.” | My uncle exclaimed with applause that I had done a good job. |
| He said, “I can’t believe this!” | He exclaimed with wonder/surprise that he couldn’t believe that. |
| She said to me, “Wow! What a pleasant weather it is!” | She exclaimed with joy that it was a very pleasant weather. |
| He said, “Good morning, Mom!” | He wished his Mom good morning. |
| He said to Mayank, “May you succeed in life!” | He prayed that Mayank might succeed in life. |
| She said to me, “Would that you were here at that time!” | She wished that I had been there at that time. |
| He said, “Raveena had a car.” | He said that Raveena had a car. |
| My boss said to me, “Don’t go there.” | My boss ordered me not to go there. |
| He said, “Oh no! I missed it.” | He exclaimed with sorrow that he had missed it. |
| He said, “Oh! I missed the chance.” | He exclaimed with sorrow that he had missed the chance. |
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise
- Mohan said, “I am very busy now.”
- I said to you, “Did you buy a watch?”
- He said, “The horse has been fed.”
- She said to him, “Can you do this work?”
- “I know her name and address,” said John.
- They said to the boy, ” you sang well.”
- “English is easy to learn,” she said.
- You said, ” Girl is here.”
- He said, “I am writing letters.”
- Pooja said, “Today is fine day.”
- “It is too late to go out,” Alice said.
- She said, “How are you?”
- He said to me, “I don’t believe you.”
- She said, “What are you?”
- He says, “I am glad to be here this evening.”
- I asked her, “Which class do you read in?”
- He said to me, “What are you doing?”
- I said to old man, “Do you like this book?”
- “Where is the post office?” asked the stranger.
- She said, ” I was present.”
- He said, “Will you listen to me?”
- She said to me, “Do you love a lot?”
- Mukesh said to Pooja, “Go away.”
- He said, “I love you”
- She said to me, “Please wait here till I return.”
- She says to them, “This is mine and that is yours.”
- “Call the witness,” said the judge.
- She said to me, “Can you speak English?”
- The speaker said, “Be quiet and listen to my words.”
Read More: MPPSC Free Study Material (English/Hindi)
🤩Follow Our Social Media Handles
YouTube 👉 https://bit.ly/36wAy17
Telegram👉 https://bit.ly/3sZTLzD
Facebook 👉 https://bit.ly/3sdKwN0
Daily Current Affairs Quiz for UPSC, MPSC, BPSC, and UPPSC: Click here

