New Article
Verb: Definition and Types of Verb
- March 14, 2023
- Posted by: Admin
- Category: English Grammar BPSC MP Patwari Exam MPPSC State PSC Exams UPPSC UPSC

Verb: Definition and Types of Verb
Definition
Definition of Verb: The Verb is a word used to express some action, feeling or existance. It tells us something about the subject in a sentence.
क्रिया की परिभाषा: Verb एक शब्द है जिसका प्रयोग कुछ कार्य, भावना या अस्तित्व को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है. यह हमें एक वाक्य में विषय के बारे में कुछ बताता है.
जैसे; सोना, जागना, पढ़ना, घूमना, नाचना, बात करना, समझना, उत्तेजित होना, मजाक उड़ाना, पूछना आदि.
दुसरें शब्दों में, Verb Kya Hai
The word which tells something about a person, thing or place is called Verb.
जो शब्द किसी व्यक्ति, वस्तु, स्थान इत्यादि के बारे में कुछ बताता है, Verb कहलाता है.
Verb Examples
- Soni reads a book. सोनी किताब पढ़ती है.
- Ankit eats sweets. अंकित मिठाई खाता है.
- I feel cold. मुझे ठंड लग रही है.
- Dasrath was a great king. दशरथ एक महान राजा थे.
- I go to school every day. मैं प्रतिदिन विद्यालय जाता हूँ.
- You run a mile every morning. आप हर सुबह एक मील दौड़ते हैं.
- Do your homework. अपना होमवर्क करें.
- Rehan plays cricket. रेहान क्रिकेट खेलता है.
- You called out my name. आपने मेरा नाम पुकारा.
- You really walked all the way back? क्या आप वाकई पूरे रास्ते वापस चले गए?
- Do the dishes. बर्तन साफ़ करो.
- I hardly ever drink enough water in a day. मैं शायद ही कभी एक दिन में पर्याप्त पानी पीता हूँ.
- She drove all the way back. वह पूरे रास्ते वापस चली गई
दिए गए वर्ब उदहारण में Verb subject की भाव को व्यक्त कर रहा है. जैसे; सोनी किताब पढ़ती है में किताब सोनी के कार्य करने की स्थिति को व्यक्त कर रहा है. इसलिए, Read एक वर्ब है. इसके अलावा Back colour में उपलब्ध सभी Words Verb के उदहारण है.
Note:
Verb हमेशा subject के नंबर और person के अनुसार वाक्य में प्रयुक्त होते है. अर्थात, subject अगर सिंगुलर होगा, तो verb सिंगुलर और यदि subject प्लूरल होगा, तो वर्ब भी प्लूरल होगा.
Types of Verb
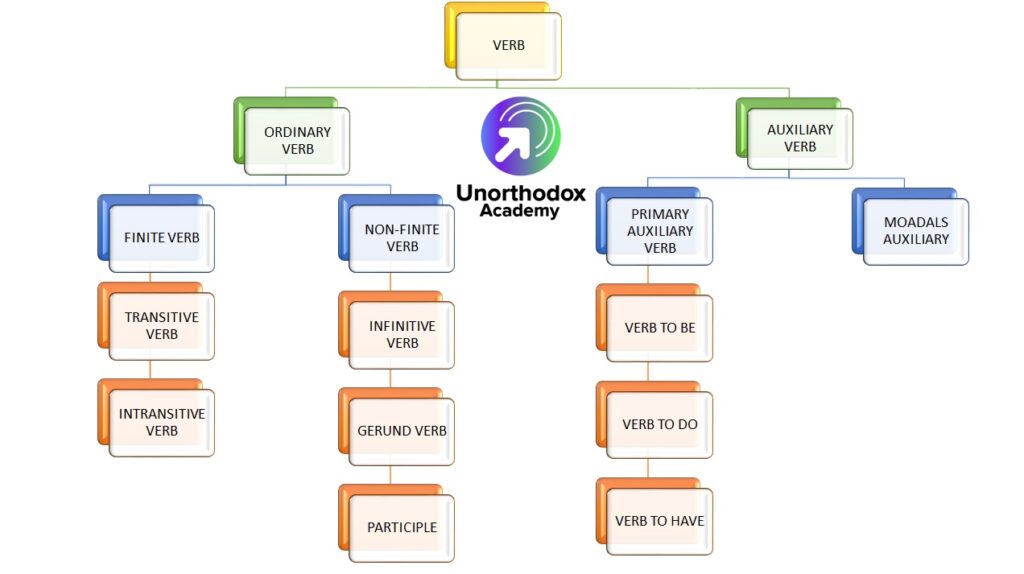
Verb को दो Major Classes में बांटा गया है. और इसी के अंतर्गत वर्ब का अध्ययन सरलतापूर्वक किया जाता है. वर्ब के कई भाग होते है और वे सभी इन्ही दो रूपों में निहित है.
- Main / Principal / Full / Ordinary / Lexical Verbs
- Auxiliary / Helping Verbs
इसके अलावे वर्ब को इस प्रकार भी विभाजित किया जा सकता है.
- Main/Base Verb
- Regular/Weak Verb
- Irregular/Strong Verb
- Transitive Verb
- Intransitive Verb
- Weak Verb
- Strong Verb
- Finite Verbs
- Non-finite Verbs
- Action Verbs
- Linking Verb
- Auxiliary Verbs
- Modal Verbs
- Reflexive Verb
- Ergative Verb
- Phrasal Verb
- Lexical Verb
- Delexical Verb
- Stative/Being Verb
- Dynamic Verb
- Non-continuous Verb
- Participle
- Gerund
- Infinitive
1. Ordinary / Main Verb (मुख्य क्रिया)
मुख्य क्रिया को लेक्सिकल क्रिया या प्रधान क्रिया भी कहा जाता है. यह शब्द मुख्यतः वाक्य में महत्वपूर्ण क्रिया को संदर्भित करता है, जो आमतौर पर विषय के होने की क्रिया या स्थिति को दर्शाता है. मुख्य क्रियाएं वाक्य में अकेले भी खड़ी हो सकती हैं, या उनका उपयोग सहायक क्रिया के साथ भी किया जा सकता है.
- I had seen the movie before.
- I want to learn English.
- He lives in Delhi.
- They play.
Main Verb की संख्या असीमित होते है. इसलिए इनका पांच रूप होता है.
| Full Verb | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 |
| To Go | go | went | gone | going | goes |
| To Eat | eat | ate | eaten | eating | eats |
| To Write | write | wrote | written | writing | writes |
| To Put | put | put | put | putting | puts |
| To Read | read | read | read | reading | reads |
| To Play | play | played | played | playing | plays |
मुख्य क्रिया यानि Main Verb की कोई सीमा नही है लेकिन इसकी अपनी एक पहचान है जिसे आसानी से पहचाना जा सकता है.
पहचान:-
किसी भी अंग्रेजी शब्द के Meaning के अंत में “ना” आए तो वह Main Verb का उदाहरण होता है. जैसे:-
- Go = जाना
- Come = आना
- Play = खेलना
- Take = लेना
- Give = देना
- Read = पढ़ना
Main Verb दो प्रकार के होते है.
- Finite Verbs
- Non-Finite Verbs
a. Finite Verbs
A finite verb is that which is limited to the number, person and tense of its subjects.
Or
A finite verb is that which changes its form according to the numer, person and tense of its subject.
Or
A finite verb is that which agrees with the number, person and tense of its subject.
Finite Verb का अर्थ सीमित होता है, यानी Finite वह Verb है जो सब्जेक्ट के Person, Number और Tense के अनुसार अपने आप को सीमित रखता है.
दूसरे शब्दों में, Finite Verb अपने सब्जेक्ट के Number, Person और Tense के साथ बदल जाता है या अपने सब्जेक्ट के Number, Person और Tense के साथ Agree करता है.
For Example:-
- I am a teacher.
- He is a student.
- They are players.
- You are singers.
दिए गए वाक्यों में “am”, “is”, तथा “are finite verbs है, क्योंकि ये Verbs अपने Subjects के Number और Person के साथ सिमित है.
विस्तार से समझने के लिए एक दूसरा उदाहरण लेते है.
- He lives in Delhi.
- I live in Patna.
- They live in Lucknow.
इस उदाहरण में live एक Finite Verb है, क्योंकि यह अपने Subject के Number और Person के साथ Agree करता है. इसीलिए Subject “He” के साथ इसमें “S” जोड़ा गया है.
Finite Verbs को दो वर्गों में बाँटा गया है.
- Transitive Verb (सकर्मक क्रिया)
- Intransitive Verb (अकर्मक क्रिया)
– Transitive Verb (सकर्मक क्रिया)
A transitive verb is a Verb that denotes an action which passes over from doer or subject to an object.
सकर्मक एक क्रिया है जो एक विशेष क्रिया को दर्शाता है जो किसी वस्तु से कर्ता या संपूर्ण विषय से होकर गुजरता है.
- Rani sang a song.
- He Wrote a letter.
- Chiku likes sweets.
तीनो वाक्यों में तिन अलग-अलग Verb क्रमशः sang, wrote और likes का प्रयोग किया गया है. इन Verbs के द्वारा action का फल केवल Subjects पर ही नही पड़ा, बल्कि एनी शब्द पर भी पड़ता है. यानि Verbs द्वारा denotes action को तो प्रभावित करते ही है साथ ही साथ Objects भी प्रभावित करते है.
– Intransitive Verb (अकर्मक क्रिया)
An Intransitive Verb is a verb that denotes an action which does not pass over to an object or that does not require an object.
Intransitive एक क्रिया है जो एक क्रिया को दर्शाती है जिसका प्रभाव केवल सब्जेक्ट पर ही पड़ता है.
Example:-
- Guddu laughs.
- Dogs bark.
- Birds fly.
दिए गए वाक्यों में Verbs द्वारा denotes action का फल subject से ही आरम्भ होकर subjects पर समाप्त हो जाता है इसलिए इसे Intransite Verb कहा जाता है.
b. Non-Finite Verb
A non-finite verb is that which is not limited to the number, person and tense of its subject.
Or
A non-finite verb is that which does not change its form according to the number, person and tense of its subject.
Or
A non-finite verb is that which does not agree with the number, person and tense of its subject.
Non-Finite Verb का अर्थ सिमित नही होता है यानि Non-Finite वह Verb है जो अपने Subject के Number और Person के साथ सिमित नही रहता है.
Example:-
- I want to learn English.
- He wants to learn English.
- They want to learn English.
Sentences में want, wants और want finite verb है जबकि to learn non-finite Verb. to learn non-finite verb इसलिए है क्योंकि यह अपने subject के Number और Person के साथ Agree नही करता है. यानि Different subjects (I, He और They) के साथ इसका Same form ही रहता है.
Note:-
Non-finite Verb को मुख्यतः तिन वर्गों में विभाजित किया है जो इस प्रकार है.
- Infinitive
- Participle
- Gerund
Infinitive — Non Finite Verb
सामान्यतः Infinitive, Verb का वह रूप है जो हमेशा To + V1 के रूप में रहता है. Verb के इस रूप पर Subject के Number तथा Person का कोई प्रभाव नही पड़ता है. अर्थात, सरल शब्दों में, Infinitive अपने पहले “To” लेकर या To के बिना भी प्रयुक्त होता है. जैसे:-
- शराब पीना बुरी बात है. To drink wine is a bad habit.
- मेरा भाई यहा रहना नही चाहता है. My brother does not want to live here.
- मुझे जाने की अनुमति दे. Allow me to go.
- मुझे जाने दो. Let me go.
- सुमन दिल्ली जाने वाला था. Suman was to go to Delhi.
- मुझे रोज यहाँ आना पड़ता है. I have to come here daily.
वाक्य में प्रयुक्त to drink, to live, to go, go, और to come, Infinitives है. क्योंकि, इनपर सब्जेक्ट का कोई प्रभाव नही पड़ा है.
Infinitive के प्रकार
प्रयोग एवं बनावट के अनुसार Infinitive को दो भागों में विभाजित किया गया है. जो इस प्रकार है.
- To – Infinitive
- Bare Infinitive
वैसा Infinitive जो अपने पहले “To” लेता है, वह To – Infinitive और जो “To” नही लेता है, वह Bare Infinitive कहलाता है. जैसे:-
- To find fault is easy. – To – Infinitive
- To walk is a good exercise. – To – Infinitive
- I bade him go. (go – Bare Infinitive)
- Let him sit there. ( sit – Bare Infinitive)
Gerund — Non Finite Verb
सामान्यतः Gerund Infinitive का वह रूप है जिसके अंत में “ing” लगा रहता है. तथा जो Noun की तरह प्रयुक्त होता है, वह Gerund कहलाता है.
- मुझे बात करना अच्छा लगता है. I like talking.
- वह बोलना रोक दिया. He stopped speaking.
- टहलना एक प्रकार का व्यायाम है. Walking is a kind of exercise.
- क्रिकेट खेलना मेरा शौख है. My hobby is playing cricket.
- वे ताश खेलने का शौखिन है. They are found of playing cards.
- उसे कहानी पढ़ना अच्छा लगता है. He likes reading story.
उदाहरण में प्रयुक्त talking, speaking, walking, playing, reading आदि Gerund है. ये वर्ब के अनुसार अपना रूप नही बदल रहे है.
Participle — Non Finite Verb in Hindi
वैसा Non Finite Verb जिसमे Verb एवं Adjective दोनों के गुण हो. अर्थात, जो दोनों के रूप में प्रयुक्त हो, वह Participle कहलाता है. दुसरें शब्दों में, ( V1 + ing / V1 + ed/ en , having + V3 ) के रूप को Participle कहा जाता है. यह Verb और Adjective के रूप में कार्य करता है. जैसे:-
- उसने मुस्कुराते हुए पूछा. He asked smiling.
- मैंने उसे सड़क पार करते हुए देखा. I saw him crossing the road.
- एक कुत्ता दौड़ रहा है. A dog is running.
- नाश्ता लेकर वह ऑफिस चला गया. Having taken breakfast, he went to the office.
- बिस्तर पर लेटकर मैं किताब पढ़ रहा था. Lying in the bed I was reading a book.
- वह रोते हुए गई. She went weeping.
Participle के भेद
प्रयोग एवं बनावट के दृष्टिकोण से Participle को तीन वर्गों में बांटा गया है.
- Present Participle
- Past Participle
- perfect Participle
Verb के जिस रूप में “ing” लगा हो, उसे Present Participle कहते है, तथा जिसमे ed/ t/ en हो, उसे Past Participle एवं जो Having + V3 रूप का पालन करता है उसे perfect Participle कहते है. जैसे:-
- He is playing cricket. (Present Participle)
- He has a smiling face. (Present Participle)
- He had finished his work. (Past Participle)
- A tiger was killed by him. (Past Participle)
- Having taken breakfast, Mohan gone to office. (perfect Participle)
- Having typed the letter, he posted it. (perfect Participle)
2. Auxiliary/ Helping Verbs (सहायक क्रिया)
Auxiliary or Helping Verbs are those that help the main verbs in the formation of tenses.
सहायक क्रियाएं वे हैं जो काल के निर्माण में मुख्य क्रियाओं की सहायता करती हैं.
For Example:-
- Aditi is eating rice.
- They have written a letter.
- Amritansh will play cricket.
- You don’t help the poor.
- Satyajit is operating the computer.
- Madhu is talking to Rajani.
दिए गए वाक्यों में Main Verb “eating, written, play आदि की tense के फार्मेशन में सहायता कर रहे है.इसलिए “is, have, do” आदि Auxiliary Verbs है.
Note:-
Auxiliaries Verbs की संख्या 24 होती है, जिसमे 11 Primary Auxiliaries Verbs और Modal Auxiliaries Verbs होते है.
| Auxiliaries | Present | Past |
| Be | Is / are / am | Was / Were |
| Do | Do / Does | Did |
| Have | Have / Has | Had |
| Can | Can | Could |
| May | May | Might |
| Shall | Shall | Should |
| Will | Will | Would |
| Must | Must | X |
| Ought to | Ought to | X |
| Need to | Need | X |
| Used to | X | Used to |
| Dare | Dare | X |
Auxiliary Verbs दो प्रकार के होते है.
- Primary Auxiliaries
- Modal Auxiliaries
Primary Auxiliary
The “primary” auxiliary verbs—be, have, and do, अंग्रेजी में सबसे अधिक प्रयोग होने वाली क्रियाओं में से हैं. इसका प्रयोग सरलता से करना लगभग कठिन है, क्योंकि प्रत्येक को एक खंड में मुख्य क्रिया के रूप में भी इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है, और प्रत्येक परिणाम के रूप में बहुलता और काल को प्रतिबिंबित करने के लिए संयुग्मित करने में सक्षम है.
Be and have का उपयोग निरंतर, perfect, and perfect continuous tenses में करने के लिए सहायक के रूप में किया जाता है. Do का उपयोग मुख्य क्रियाओं को नकारात्मक बनाने या प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य बनाने के लिए किया जाता है, और इसका उपयोग वाक्य में जोरदार बनाने के लिए भी किया जा ता है.
मुख्य सहायक क्रिया का रूप
| Be Conjugations | Auxiliary example sentence |
|---|---|
| be | “You must be joking.” |
| am | “I am moving to Germany next month.” |
| are | “We are leaving tomorrow morning.””Are you working later?””Where are they going?” |
| is | “She is wondering where we’re going.” |
| was | “I was talking to my brother yesterday.””It was raining quite hard last night.” |
| were | “We were looking for a new place to live.””You were thinking of running away?””When were they planning on electing a new president?” |
| been | “Everyone has been worrying about their jobs.” |
| being | “I could tell that the instructor’s patience was being tested by the students.” |
| Have Conjugations | Auxiliary Example sentence |
|---|---|
| have | “I have been to this part of town before.” |
| has | “It has been raining for over an hour now.” |
| had | “They had been confident in the project’s success.” |
| having | “Having worked his whole life, Larry relished the thought of retirement.” |
| Do Conjugations | Auxiliary Example sentence |
|---|---|
| do | “Do be careful.” |
| does | “Does he know what he’s talking about?” |
| did | “We didn’t know any better.” |
Primary Auxiliaries के अंतर्गत आने वाले Verbs निम्न है.
- Verb “to be” = is, are, am, was and were
- Verb “to do” = do, does and did
- Verb “to have = have, has and had
Modal Auxiliaries Verb
सहायक क्रियाओं का एक छोटा समूह, जिसे मोडल वर्ब कहा जाता है, का उपयोग केवल सामान्य क्रियाओं के संयोजन में किया जाता है. एक क्रियात्मक क्रिया दूसरी क्रिया के अर्थ को साधारण तथ्य से अलग किसी संभावना में बदल सकती है. मोडल का प्रयोग अनुमति, क्षमता, भविष्यवाणी, संभावना या आवश्यकता को व्यक्त करने के लिए होता है.
मोडल वर्ब का प्रयोग निम्न प्रकार किया जाता है:
| Modal Auxiliary | Modal Auxiliary + Main Verb |
|---|---|
| can | I can lift this forty-pound box. (ability) |
| could | I could beat you at chess when we were kids. (past ability) |
| may | I may attend the concert. (uncertain future action) |
| might | I might attend the concert (uncertain future action—same as may) |
| shall | I shall go to the opera. (intended future action) |
| should | I should mail my RSVP. (obligation, same as ought to) |
| will | I will get an A in this class. (intended future action) |
| would | I would like the steak, please. (preference) |
| must | We must be on time for class. |
| ought to | I ought to mail my RSVP. (obligation, same as may) |
Modal Verb के फॉर्म
| Affirmative | Negative | Contracted forms |
| can | cannot | can’t |
| could | could not | couldn’t |
| may | may not | — |
| might | might not | — |
| ought to | ought not to | oughtn’t to |
| need | need not | needn’t |
| shall | shall not | shan’t |
| should | should not | shouldn’t |
| will | will not | won’t |
| would | would not | wouldn’t |
Modal Auxiliaries के अंतर्गत आने वाले Verbs निम्न है.
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Shall
- Should
- Will
- Would
- Ought to
- Used to
- Need
- Must
- Dare
Note:-
- Do के किसी भी रूप के साथ V1 का प्रयोग किया जाता है.
- Modal Auxiliaries Verbs किसी वाक्य के Subject के Number और Person से प्रभावित नही होता है.
- Modal Auxiliaries Verbs का प्रयोग बिना main Verb के नही किया जा सकता है.
Read More: MPPSC Free Study Material (English/Hindi)
🤩Follow Our Social Media Handles
YouTube 👉 https://bit.ly/36wAy17
Telegram👉 https://bit.ly/3sZTLzD
Facebook 👉 https://bit.ly/3sdKwN0
Daily Current Affairs Quiz for UPSC, MPSC, BPSC, and UPPSC: Click here
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is Verb?
A verb is a word that indicates a physical action (e.g., “drive”), a mental action (e.g., “think”), or a state of being (e.g., “exist”). Every sentence contains a verb. Verbs are almost always used along with a noun or pronoun to describe what the noun or pronoun is doing.
How many types of Verb are there?
Verbs are mainly of three types, which are as follows: Finite Verb, Non-finite Verb and Auxiliary Verb.
How to recognize Verb?
The word which tells something about a person, thing, place etc. is called Verb. Like, waking up, reading, walking, dancing, talking etc.

